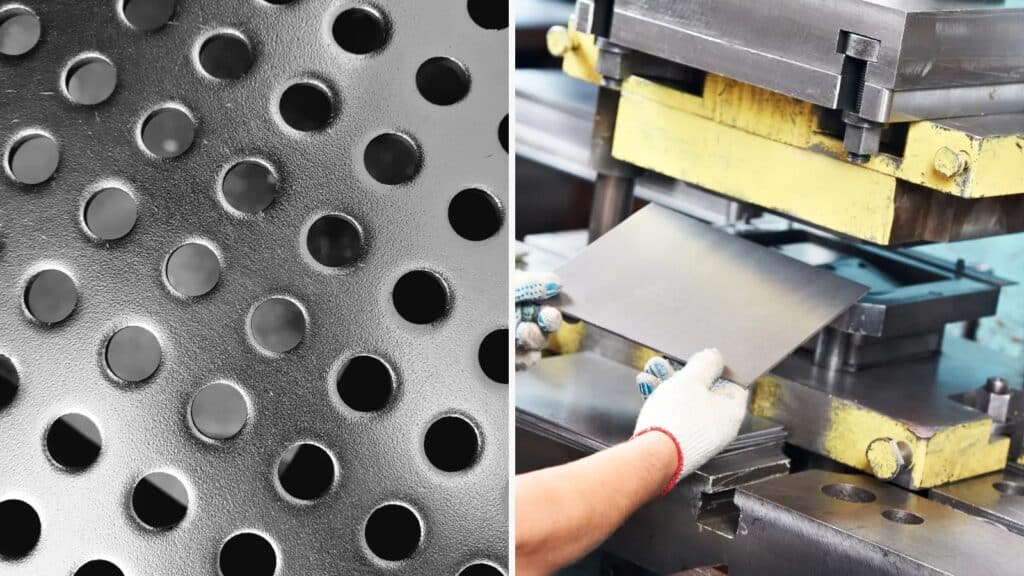
More and more industrial sectors are seeking effective solutions to transform raw materials into functional, durable, and precise components. In this context, metal stamping has become one of the most widespread and versatile techniques. Although it may seem like a simple process at first glance, it involves a complex combination of technology, materials, and expertise. At Bericht, as experts in this type of manufacturing, we explain everything you need to know.
Introduction to Metal Stamping
Metal stamping is a manufacturing process that involves deforming metal sheets using pressure to obtain specific shapes. This procedure is performed using dies and presses, allowing for the production of everything from simple parts to technically complex components. Thanks to its precision and repeatability, it has become a perfect option for mass production in sectors such as automotive, electronics, machinery, or consumer goods.
Core Processes in Metal Stamping
Metal stamping encompasses a set of industrial methods whose choice depends on the part’s design, the type of material, and the desired production volume.
Cold Stamping vs. Hot Stamping
Metal stamping can be performed either cold or hot. In the cold version, deformation occurs at room temperature. It is the most common method since it maintains tight tolerances and reduces energy consumption. It is used for mild steels, aluminum, or brass. In contrast, hot stamping is carried out at high temperatures to improve metal ductility, which is essential for more resistant materials such as alloy steel. This variant is used when it is necessary to work with thick materials or complex shapes without compromising structural strength.
Key Techniques: Cutting, Blanking, Deep Drawing, Bending, and Punching
These operations allow transforming the metal sheet into a part with the desired final geometry:
- Cutting: separates the part from the rest of the material through direct die action.
- Blanking: removes part of the metal using a die with specific shapes.
- Deep drawing: transforms the sheet into a volume without removing material, as in cans or casings.
- Bending: modifies the angle of a section without breaking the continuity of the part.
- Punching: creates functional or assembly holes in specific locations.
Each of these operations, alone or combined, helps optimize design according to the part’s final use.
Equipment Used: Mechanical, Hydraulic, and Automatic Presses
The machines used in metal stamping are essential to achieve the desired precision:
- Mechanical presses: provide high speed and are used for mass production of thin parts.
- Hydraulic presses: apply constant pressure, ideal for thicker or more complex parts.
- Automatic presses: combine speed with computerized control, maximizing efficiency and repeatability.
The choice of one type or another depends on the part’s design, volume, and material.
Cold stamping is one of the most popular options due to its ability to maintain tight tolerances and low energy consumption. This process, performed at room temperature, is ideal for materials such as mild steel and aluminum. For more information on cold stamping, visit our dedicated page on Cold Stamping of Metal Parts.
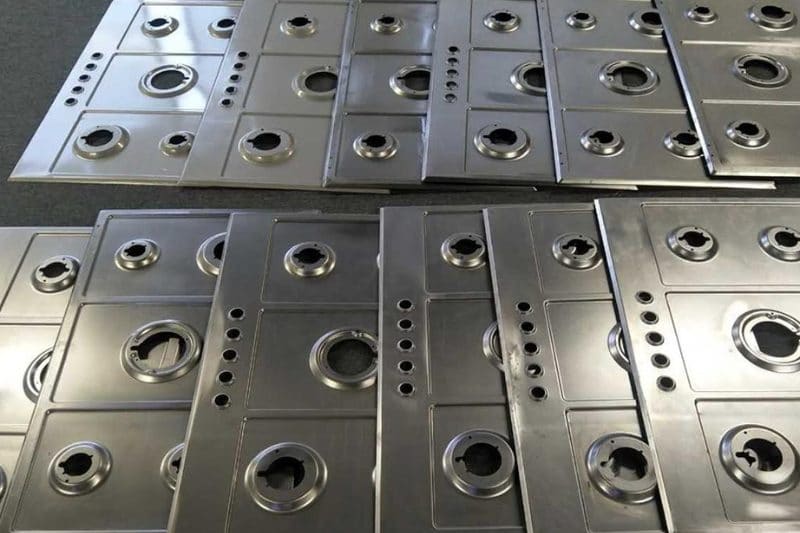

Common Materials in Metal Stamping
The choice of material directly influences the final result of the part, its mechanical behavior, and its wear resistance.
- Steel stamping: used in structures requiring strength, such as vehicle chassis or structural parts. It provides rigidity and durability.
- Aluminum stamping: used when lightness is needed without sacrificing rigidity. Common in the aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries.
- Sheet metal stamping: includes various thin materials adaptable to different shapes. Its flexibility suits diverse designs in sectors like furniture or electronics.
- Other materials: copper, brass, titanium, or even precious metals may be used depending on conductivity, corrosion resistance, or aesthetic requirements.
This diversity allows the technique to be applied in sectors with very different demands, from technical precision to visual appeal.
Stainless steel is one of the most requested materials in metal stamping due to its corrosion resistance and durability. This material is commonly used in sectors like automotive and appliance manufacturing. If you’re interested in learning more about stainless steel and its applications, visit our full article on Stainless Steel vs. Anti-Corrosion Coated Steel.
Industrial Applications of Metal Stamping
Metal stamping is integrated into a vast range of industrial processes. In automotive, it enables the manufacturing of panels, supports, reinforcements, and structural parts. In electronics, it is used for components such as casings, contacts, and connectors. In appliances, it is used for both functional and decorative parts. It also has applications in the construction, metal furniture, HVAC, medical, and even defense industries. Its versatility and efficiency make it an essential technique for mass production.
In the automotive industry, metal stamping is crucial for manufacturing panels and structural parts. Thanks to its precision and versatility, it’s possible to create lightweight and strong components that meet strict safety standards. If you’d like to learn more about how stamping is used in the automotive sector, don’t hesitate to check out our article on Hot Rolled Steel.
Advantages of Metal Stamping in Industrial Production
One of the main reasons for using metal stamping is the range of advantages it offers for industrial processes that require volume, quality, and efficiency.
- High precision: dies and molds ensure tight tolerances even in large production runs.
- Production speed: once the machine is set, the process can be repeated very quickly.
- Consistency: all produced parts maintain identical characteristics, improving assembly and reducing waste.
- Versatility: it adapts to various materials, designs, and quantities without compromising quality.
- Cost reduction: by optimizing material usage and automating the process, operational costs are lowered.
Thanks to all these advantages and its wide range of uses, this technique is one of the favorites in modern manufacturing. At Bericht, we develop tailored solutions to make your production more efficient and competitive.
Frequently Asked Questions About Metal Stamping
You may still have some questions about metal stamping, so in this section, we answer some of the most common ones:
What is the difference between cold and hot stamping?
Cold stamping is performed at room temperature, allowing for greater dimensional precision. In contrast, hot stamping is done at high temperatures to facilitate the deformation of harder or thicker materials without cracking.
Which metals are best suited for stamping?
Metal stamping is compatible with a wide range of materials. The most commonly used are steel, aluminum, and brass, although copper, titanium, and other metals are also used depending on the design needs.
What are the main applications of metal stamping?
From structural panels to electrical connectors. It is found in automotive, electronics, construction, appliances, and many other sectors.
What advantages does stamping offer compared to other forming processes?
Unlike other methods, metal stamping allows for large-scale production with high precision and efficiency, optimizing costs without sacrificing final quality.
How is quality controlled in metal stamping?
During metal stamping, dimensional checks, visual inspections, hardness tests, and integrity checks are carried out to ensure each part meets the required technical and safety standards.